Quad Pyramid Surface Area Calculator
This online calculator calculates the surface area of a quadrilateral pyramid using the lengths of its bases and one of the following parameters: length of the edge, angle of inclination of the faces, or height of the pyramid.
This content is licensed under Creative Commons Attribution/Share-Alike License 3.0 (Unported). That means you may freely redistribute or modify this content under the same license conditions and must attribute the original author by placing a hyperlink from your site to this work https://planetcalc.com/10049/. Also, please do not modify any references to the original work (if any) contained in this content.
The surface area is the total area of all the faces of the pyramid. The calculator accepts inputs for the lengths of the bases and the chosen parameter and then calculates the surface area of the pyramid using the appropriate formula. You can find all used formulas below the calculator.
Quadrilateral pyramid
In the formulas below we will use the following notations:
a - the length of the first side of the base
b - the length of the second side of the base (for a square it will be equal to the first one)
h - the height of the pyramid
r - the edge of the pyramid
d - the base diagonal
e - the height of the triangle formed by the side edges, that is, the height, dropped from the top of the pyramid to its side
α - the angle of inclination of the pyramid edge (the angle between the height of the triangle of the side face and the plane of the base)
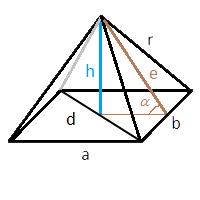
In all cases, the area of the base is calculated trivially by multiplying the lengths of the sides of the base. Below we will consider finding the areas of side faces for different cases.
Surface area of a pyramid through height
-
Find the height of the triangle formed by the side face. We use the Pythagoras theorem on a right triangle formed by the height of the pyramid, the height of the side face triangle, and the projection of the height of the triangle onto the base plane. The length of the projection is obviously half the length of the opposite side. Thus, the height of the triangle dropped on the side a
The height of the triangle, dropped on the side b
-
Find the area of the side faces, using the formula for the area of an isosceles triangle
- The total area of the side faces
The surface area of the pyramid through the angle of inclination
Calculation through one angle of inclination is possible only if the base of the pyramid is a square (otherwise you would have to specify two angles). Accordingly, side a is equal to side b, and all faces are the same.
-
Find the height of the triangle formed by the side face by dividing the length of the projection on the base plane by the cosine of the angle of inclination
- Find the area of the side face, using the formula for the area of an isosceles triangle
.
The total area of the side faces is obtained by multiplying the area of one face by 4.
The surface area of the pyramid through the length of the edge
There is a restriction here: the length of the edge must be greater than half of the base diagonal (otherwise it is not a pyramid)
-
Find the height of the triangle formed by the side edge. Use Pythagoras' theorem on the right triangle formed by the pyramid's edge, the height of the side edge triangle, and half of the side on which the height is dropped. Thus, the height of the triangle dropped on the side a
The height of the triangle, dropped on the side b
-
Find the areas of the side faces, using the formula for the area of an isosceles triangle
- The total area of the side faces
Comments