Unfolding a 3D sphere to 2D shapes
If you want to made a DIY sphere, you need to unfold the sphere to 2D shapes, or, more strictly speaking, approximate the sphere using petals, or "orange peels" (also called the lunes) on the plane. The calculator calculates basic parameters of such 2D peel and displays coordinates of points for drawing one peel on a plane.
This content is licensed under Creative Commons Attribution/Share-Alike License 3.0 (Unported). That means you may freely redistribute or modify this content under the same license conditions and must attribute the original author by placing a hyperlink from your site to this work https://planetcalc.com/6066/. Also, please do not modify any references to the original work (if any) contained in this content.
The calculator calculates the parameters of the sphere peel on the plane. The picture below illustrates the problem.
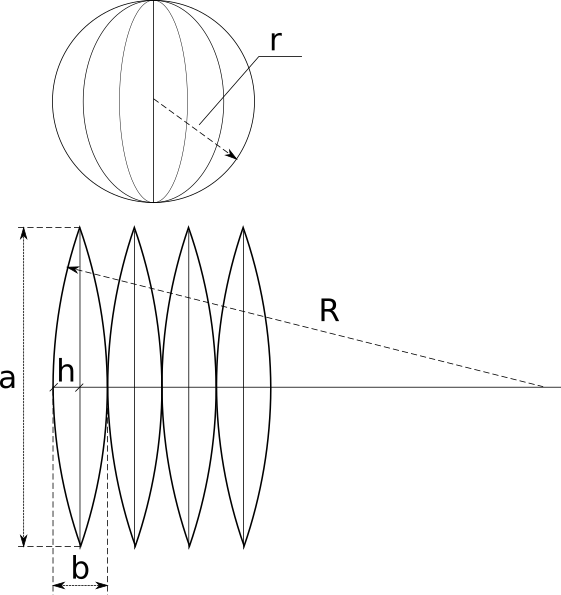
So, we know the radius of the sphere r and the number of "peels" into which we want to divide it n. To describe the peel, we need to find the height of the "peel" a, the width of the "slice" b, and the radius R of the large arc on which the "peel" is built. As usual, the calculation formulas and explanations are given below the calculator.
Unfolding a 3D sphere
Everything is clear with the height - it is half the length of the circle, which can be obtained by crossing the sphere with a plane passing through the centre. Thus,
.
The width is also clear - it is the part of the same circle obtained by dividing the whole circle into n parts:
.
The radius of the arc can be calculated from the length of the chord (that's a) and the height of the segment (that's h=b/2) using the following formula (see Circular segment).
In principle, having found a and b, it is not even necessary to count the radius R - it can be found by intersection, as illustrated by the following picture.
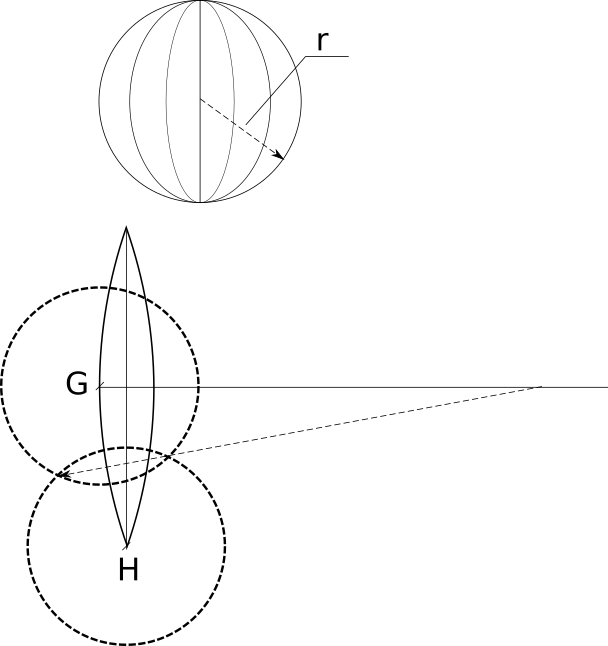
To find the radius from points G and H, we need to draw two circles so that they intersect - the line drawn through the intersection points will intersect the midline at the point of the centre of the circle, on the arc of which G and H lie.
Comments